Data Augmentation using DCGANs
Research on dataset augmentation through generative adversarial networks
[Code]
This project explores the use of Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Networks (DCGANs) for dataset augmentation, targeting scenarios with extremely limited data availability. Implemented entirely from scratch based on the original DCGAN paper, the project experiments with advanced techniques, such as Wasserstein loss, varying training routines, and custom layer configurations.
The study successfully generates realistic synthetic images using just 365 training samples, demonstrating the potential of GANs in improving model performance for data-scarce applications. Additionally, a variant of the architecture was applied to generate anime-style faces, showcasing the versatility of the approach.
Research Highlights
Key Contributions
- Paper Implementation: Fully implemented the original DCGAN paper from scratch, adapting the architecture for custom datasets.
- Limited Data Experimentation: Achieved high-quality results with only 365 training images, showcasing the robustness of the approach.
- Advanced Techniques: Explored Wasserstein loss (W-Loss), varied training routines, and custom layer configurations to enhance performance.
- Generative Versatility: Applied the model to generate both domain-specific images (dataset augmentation) and anime-style faces.
Methodology
1. Problem Statement
In data-scarce scenarios, machine learning models often struggle to generalize due to limited training data. This research aims to augment small datasets by generating realistic synthetic samples, improving model robustness for downstream tasks.
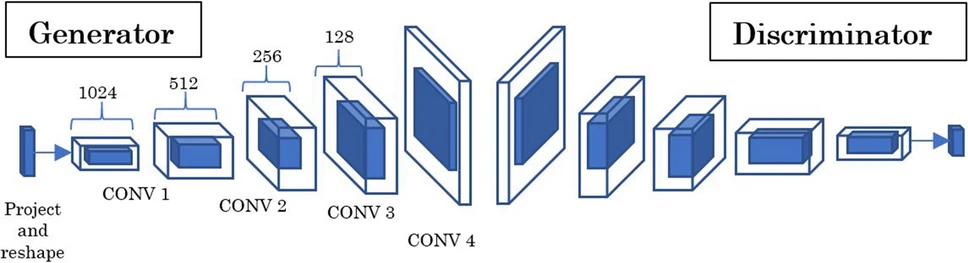
2. GAN Architecture
- Implemented a Deep Convolutional GAN (DCGAN) architecture based on the original paper, introducing:
- Custom layer configurations for domain-specific adaptations.
- Wasserstein loss to improve training stability and diversity in generated images.
- Multiple training routines to optimize adversarial performance.
3. Dataset and Training
- Dataset: Used a small dataset of 365 images for training, preprocessed to ensure consistency in size and quality.
- Training Pipeline: Conducted extensive hyperparameter tuning, including:
- Experimentation with different layer depths and kernel sizes.
- Comparative studies with and without W-loss.
- Evaluation of convergence across varying batch sizes and optimizers.
4. Extensions
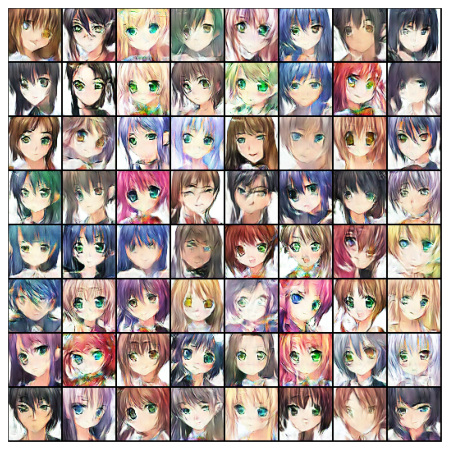
- Adapted the architecture to create an anime-style face generator, showcasing the ability of DCGANs to transfer learning across domains.
Results
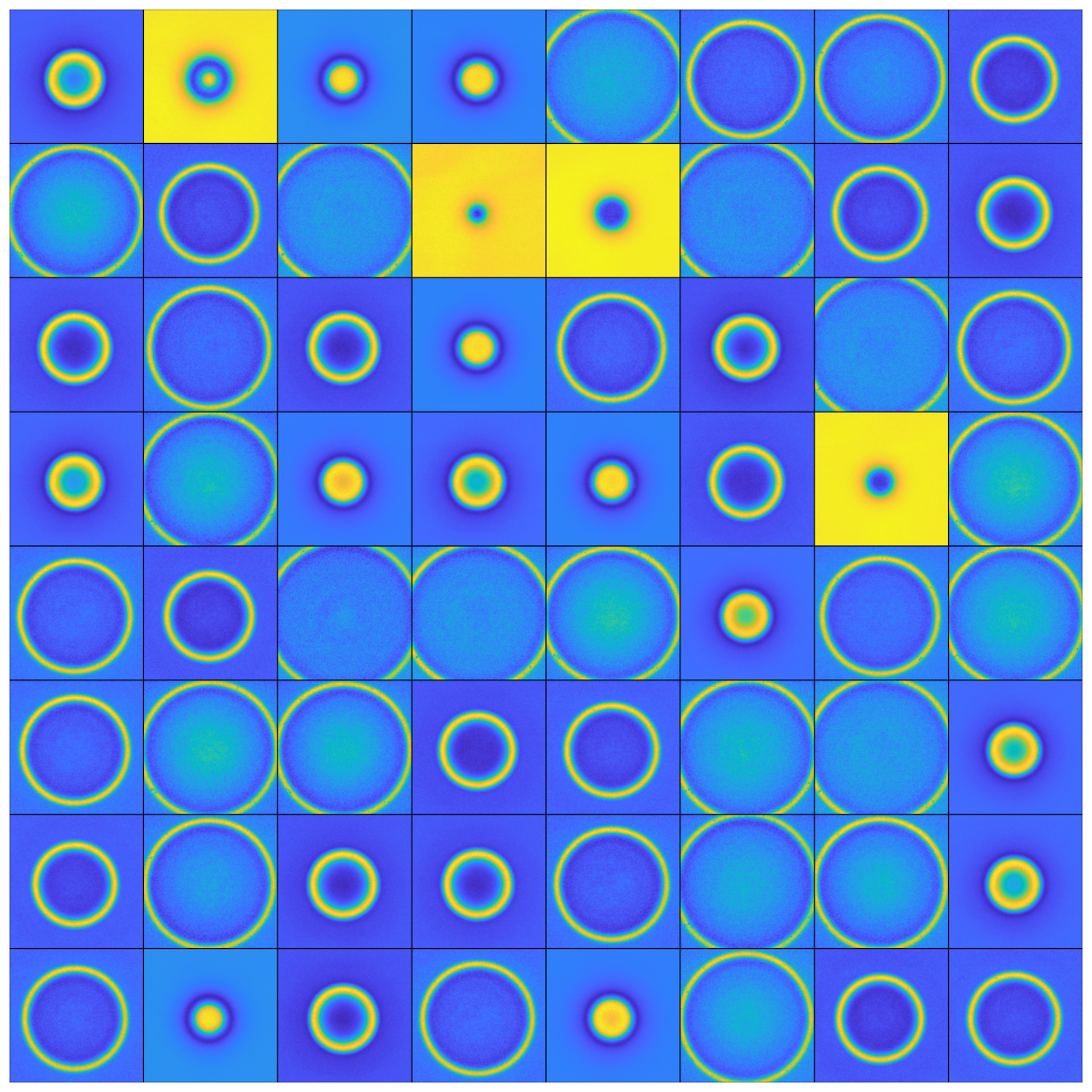
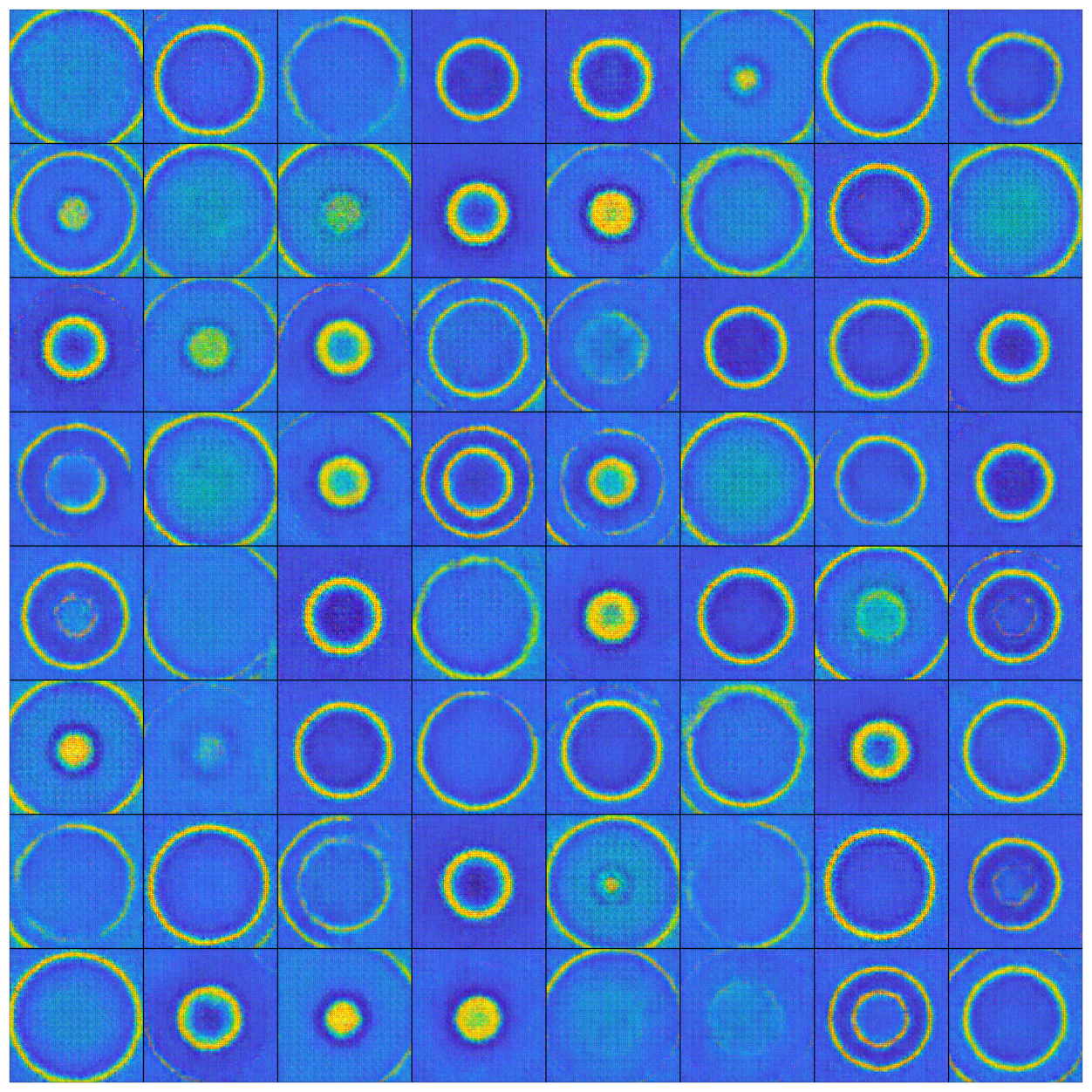
Anime Face Generator Output:

Insights
- Quality with Limited Data: The DCGAN architecture performed remarkably well, generating diverse and realistic images from just 365 samples.
- Effectiveness of W-Loss: Wasserstein loss proved essential for stabilizing training and ensuring variability in outputs.
- Generalization Across Domains: The anime face generator experiment highlighted the adaptability of the model for creative applications.
Future Work
- Improved Stability: Incorporating advanced GAN techniques like Progressive Growing or StyleGAN to enhance training stability and output diversity. Also look into Variational Autoencoders.
- Broader Applications: Applying the methodology to other domains like medical imaging, where data scarcity is common.
- Collaborative Generators: Exploring GAN architectures for simultaneous multi-class data generation.