Multimodal Price Regressor
Smart product price prediction - Amazon ML Challenge 2025
[Code] [Data]
As part of team SPAM_LLMs, we achieved 6th place overall in the Amazon ML Challenge 2025, a national competition focused on smart product pricing. Our solution secured the 3rd position on the public leaderboard and 5th on the private leaderboard.
This project showcases a multimodal learning approach to predict product prices from text descriptions and images. By using large, pre-trained embedding models without fine-tuning, our architecture effectively processed complex, real-world e-commerce data to achieve high accuracy.
Competition Highlights
Key Achievements
- Top National Ranking: Finished 3rd (Public LB) and 5th (Private LB), placing us among the top 6 teams in a highly competitive national challenge.
- Advanced Multimodal Architecture: Designed and implemented a novel system that processes text and image data in parallel to predict prices.
- Strategic Model Selection: Demonstrated that large, frozen pre-trained models (Qwen-3-4B, Siglip2, DinoV3) can outperform fine-tuned smaller models, providing a crucial performance edge.
- Effective Data Preprocessing: Developed a comprehensive pipeline for cleaning and normalizing noisy catalog data, which was critical for model performance.
Methodology
1. Business Problem
In e-commerce, setting the optimal price for products is vital for success. The challenge was to create a machine learning model that analyzes product details from text and images to accurately predict its price, tackling complexities like brand value, specifications, and quantity.
2. Data Handling & Preprocessing
- Transformation: Applied a log1p transformation to the right-skewed price data to normalize its distribution.
- Text Cleaning: Processed the
catalog_contentby stripping it into descriptions, bullet points, and quantity. We also standardized inconsistent units (e.g., “g,” “gm” to “grams”) and converted numbers to words to improve embedding quality. - Feature Selection: To handle large text fields, we prioritized using the product description if available, otherwise defaulting to the top five bullet points.
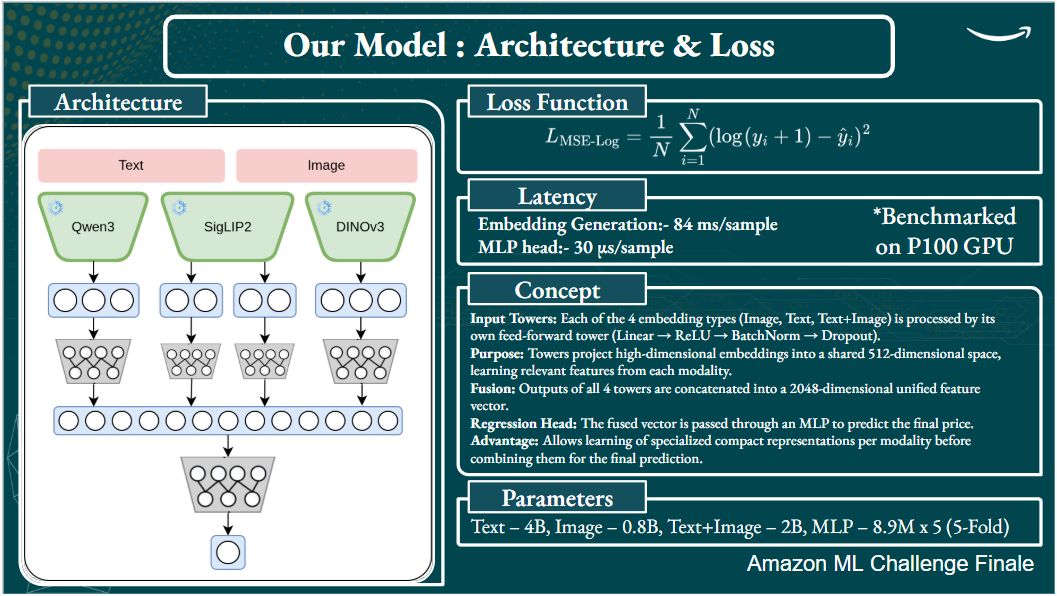
3. Multimodal Architecture
- Embedding Generation: Utilized powerful, pre-trained models to generate high-quality embeddings for each modality:
- Text: Qwen-3-4B
- Text + Image: Siglip2 Giant
- Image: DinoV3
- Modality-Specific Networks: Fed the embeddings from each modality into separate, dedicated neural networks. This allowed the model to learn modality-specific representations before fusing the information.
- Final Regressor: Concatenated the outputs from the modality-specific networks and passed them to a final regression head to predict the log-transformed price.
4. Training and Evaluation
- Loss Function: Employed a Log-based Mean Squared Error (MSE) Loss, which is well-suited for log-transformed targets.
- Evaluation Metric: The competition used the Symmetric Mean Absolute Percentage Error (SMAPE), where a lower score is better.
Insights & Conclusion
- Power of Large Models: Our success showed that using larger, state-of-the-art pre-trained models, even without fine-tuning, can provide superior feature representations compared to fine-tuning smaller, distilled models.
- Multimodality is Key: Integrating image data provided a significant signal that purely text-based models might miss, confirming the value of a multimodal approach for complex real-world problems.
- Architecture Matters: Using modality-specific networks to process embeddings before concatenation was a key architectural decision that improved training stability and overall performance.
Team Members
This was a collaborative effort by SPAM_LLMs (IIT ISM Dhanbad):
- Manav Jain [LinkedIn]
- Karaka Prasanth Naidu [LinkedIn]
- Alok Raj [LinkedIn]
- Rudraksh Sachin Joshi [LinkedIn]